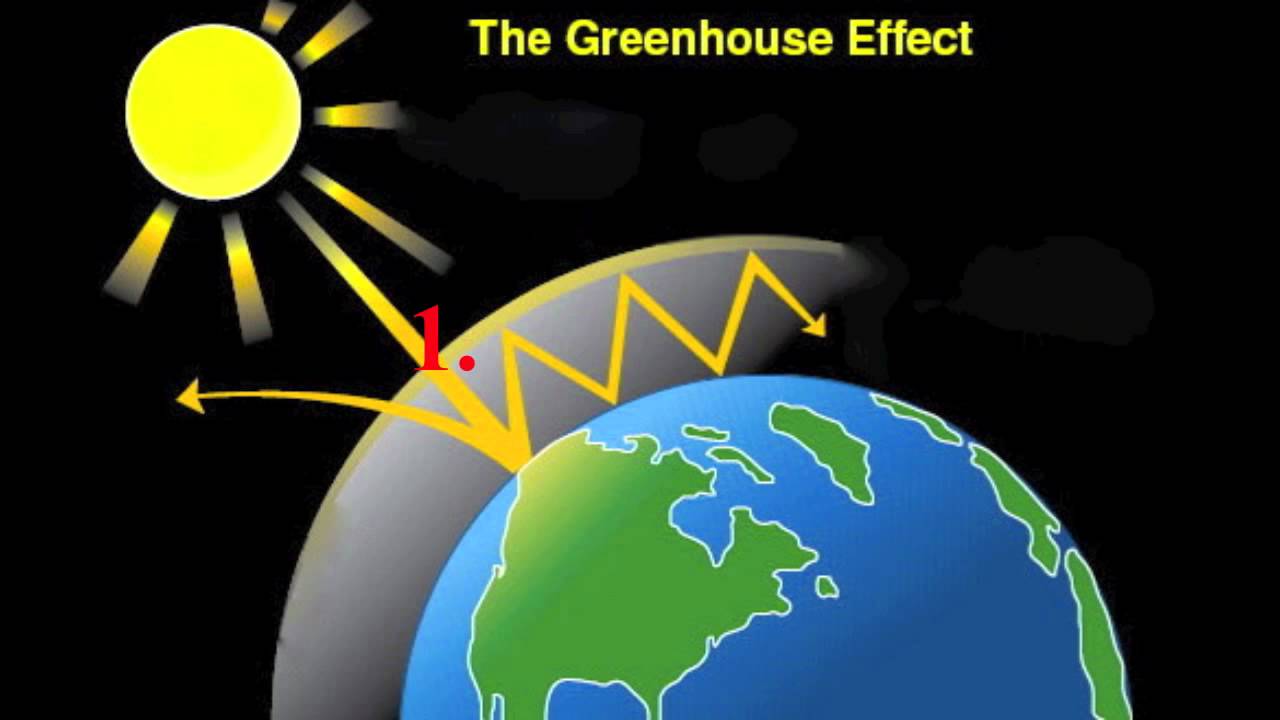
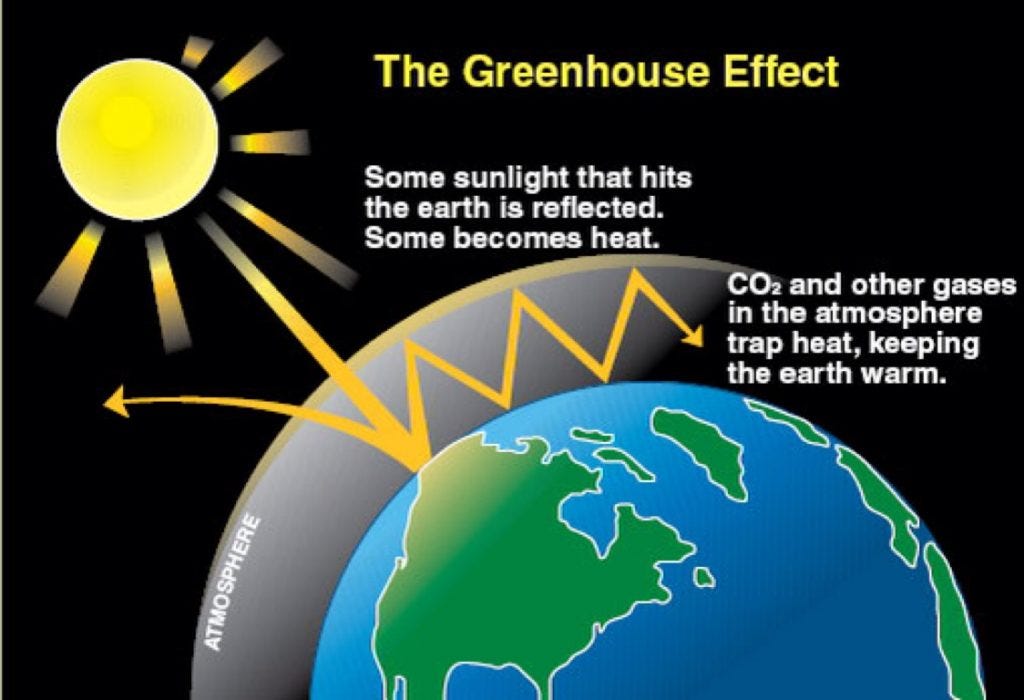
The ability of certain gases, greenhouse gases, to be transparent to inbound visible light from the sun, yet opaque to the energy radiated from the earth is one of the best still events in theGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician JosephA greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared (IR) radiation and radiates heat in all directions Greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere

Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education
What are the 4 major greenhouse gases
What are the 4 major greenhouse gases- A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere By increasing the heat in theWhat are "greenhouse gases?" The transparent windows of a greenhouse (or a car parked in the sunlight) transmit the warming visible rays of the sun, prevent the resulting warm air from leaving, and hence maintain a warmer environment inside than outside the structure In the Earth's atmosphere, some trace gases absorb infrared radiation




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
Climate change includes both global warming driven by humaninduced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting largescale shifts in weather patterns Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the midth century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale The largest driver of warming isThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsGreenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gases
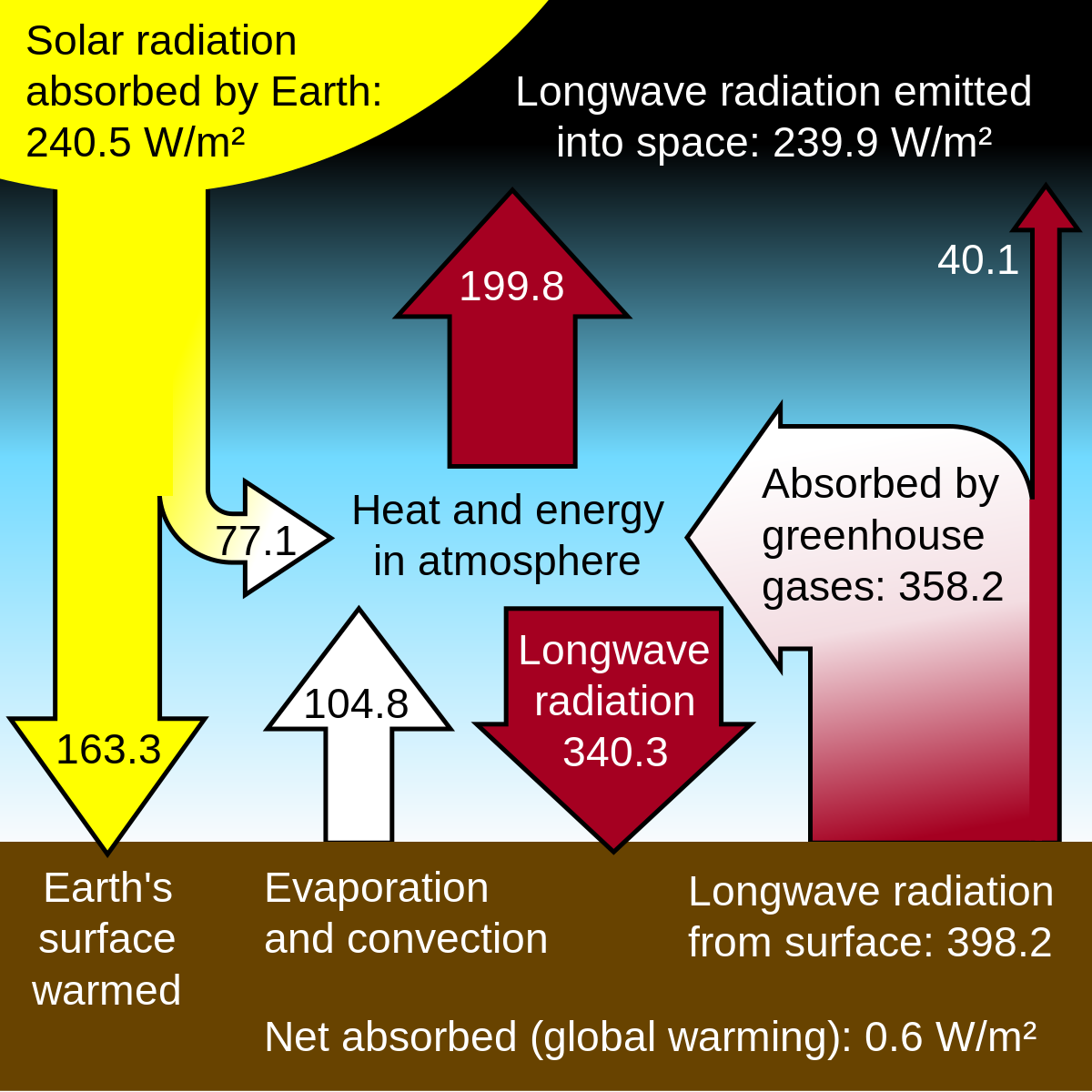
The climate effect of the changes in all the longlived greenhouse gases in the atmosphere combined can be expressed as an enhancement of the net radiation, or radiative forcing CO 2 is the largest contributor to this, but other gases also make substantial and increasing contributions Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeWater vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the Earth's atmosphere Infrared radiation that gets absorbed and reflected by the Earth's surface gets trapped and reflected back to the Earth's surface by greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere in a process known as the "greenhouse effect"
Check out our video on "Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming" by Letstute This Video covers What is Global Warming?Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
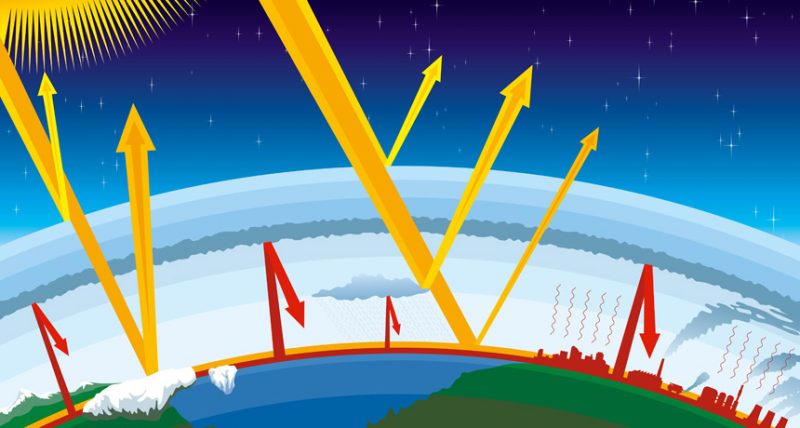




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
How do greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect?How do greenhouse gases affect earth?When it comes to climate and environmental science, the earth is very much like the car, and greenhouse gases are very much like the windows Greenhouse gases allow sunlight to




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons
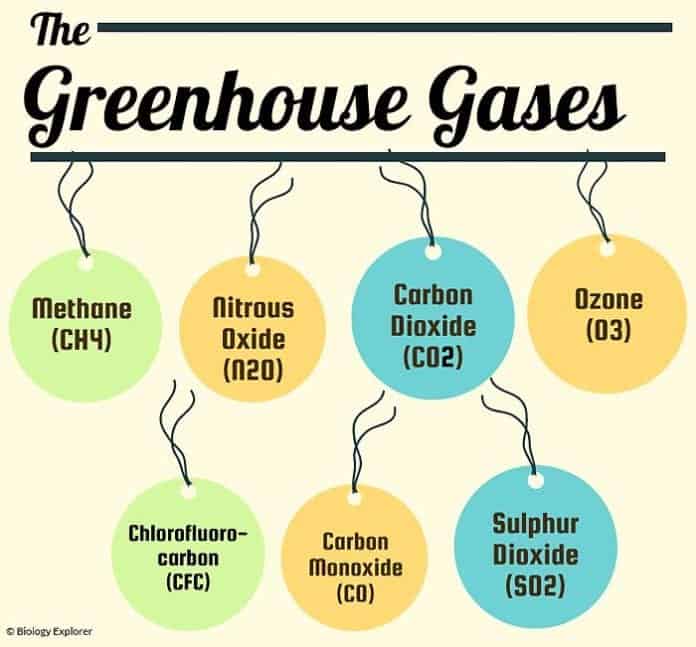
Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth's average temperature would be about 60º F colder Because of how they warm our world, these gases are referred to as greenhouse gasesOf the six greenhouse gases, three are of primary concern because they're closely associated with human activities Carbon dioxide is the main contributor to climate change, especially through the burning of fossil fuels Methane is produced naturally when vegetation is burned, digested or rotted without oxygen Oil and gas production, cattleGreenhouse gases (GHG) are gaseous compounds that can emit ultraviolet radiation within a certain thermal infrared range 76 Greenhouse gases retain high temperatures in the lower atmosphere, thus allowing less heat to escape back to space This subsequently results in the greenhouse effect and global warming




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
Greenhouse effect the insulating effect of atmospheric greenhouse gases (eg, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, etc) that keeps the Earth's temperature about 60 °F (16 °C) warmer than it would be otherwise cf enhanced greenhouse effectPlanet Earth is warm enough to sustain life thanks to gases in the planet's atmosphere that hold heat These gases are called greenhouse gases because they act just like a greenhouse — trapping the heat inside the planet's atmosphere, making the average temperature on Earth 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius)Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube
Edited By Professor M Mercedes MarotoValer and Dr Curtis M Oldenburg Impact factor 1979 19 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics) 78/112 (Energy & Fuels) 40/53 (Engineering, Environmental) 162/265 (Environmental Sciences) Online ISSNWhat contributes to the greenhouse effect?What is Green House




Pdf Does The Swedish Consumer S Choice Of Food Influence Greenhouse Gas Emissions Nils Brandt Academia Edu



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities suchWhat is the greenhouse effect?




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Finals Environmental Science
What effect does the greenhouse effect have on the earth's surface temperature?Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that allow sunlight to pass through and reach the Earth's surface Some of this sunlight is captured as heat on Earth, and some of it is radiated backGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth This process maintains the Earth's temperature at around 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would otherwise be, allowing life on Earth to exist Enhanced




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
REDUCTION IN GREENHOUSE GASES LESSON 38 REDUCTION IN GREENHOUSE GASES Adaptation and mitigation are the two types of policy responses that the Government, industry and other entities can take to address the global warming Mitigation is a preventive action while adaptation is a response to the ills that global warming would causeWhat is the relationship between global warming and the greenhouse effect? Methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) are longlived greenhouse gases (GHG), with atmospheric lifetimes of 12 and 121 years, respectively Considering their radiative forcing, CH 4 and N 2 O have a 100year time horizon global warming potentials (GWP) of 28 and 265 CO 2 equivalent (CO 2 eq), respectively 41




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect, which leads to climate change by warming global temperatures Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and water vapor Greenhouse gases concentrations have been stable over the past 10 000 years until several of For dairy and beef cattle combined, highimpact providers released about 12 times as many greenhouse gases as lowimpact producers, Poore and colleague Thomas Nemecek report in the June 1 ScienceThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Runaway Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
The inventory also reports indirect greenhouse gases but they are not included in New Zealand's greenhouse gas total These gases do not have a direct warming effect, but react with other gases in the atmosphere and increase the concentration of direct greenhouse gases The indirect gases are oxides of nitrogen (NOx) sulphur dioxide (SO2)Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere Greenhouse gas Greenhouse gases (GHG) are gases in the atmosphere that capture and reflect heat back to the Earth, and act like the glass roof of a greenhouse The Earth naturally has greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, however there are now more greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere due to human activities such as power stations, motor



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
Sylvie is a greenhouse gas analyst at a company called Ecometrica, where she helps companies measure their greenhouse gas footprints She has worked in the sustainability field in one form or another since finishing university (first getting a bachelors in environmental science and then a masters in environmental policy) The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere The gases act like the glass walls of a greenhouse—thus the name, greenhouse gas




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases are defined as 'gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and reemit infrared radiation' From International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 01 Related terms Methane;Greenhouse gases emitted by human activities alter Earth's energy balance and thus its climate Humans also affect climate by changing the nature of the land surfaces (for example by clearing forests for farming) and through the emission of pollutants that affect the amount and type of particles in the atmosphere



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Environment Air Pollution Global Warming Facts Effects Of Global Warming Ozone Layer




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
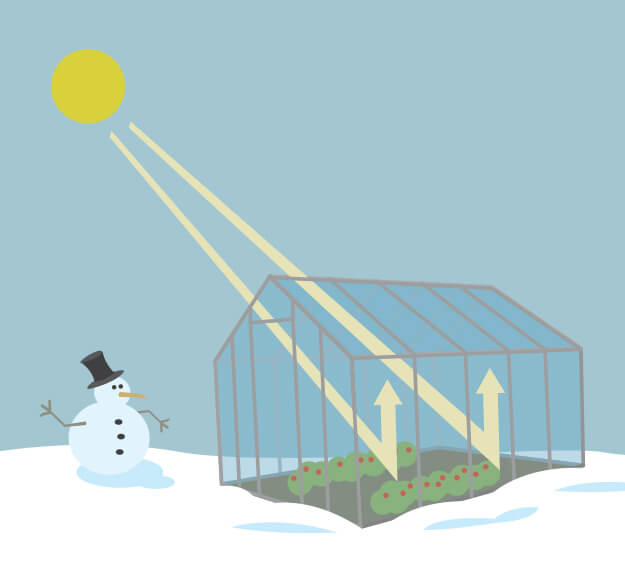




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



1




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



A Definition Of Environmental Science




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming




Environmental Science Chapter 13 Review Chlorofluorocarbons Compounds That Contain Chlorine Cause Ozone Destruction In Upper Atm Climate Described Ppt Download




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




What Is Global Warming Live Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science



Http Www Campbellcountyschools Org Userfiles 1591 Greenhouse effect global warming lab Pdf



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Semester One Final




Environmental Science Notes Outlineunit 16 Climate Change Docsbay



3




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Energy Efficency




Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Energy Efficency
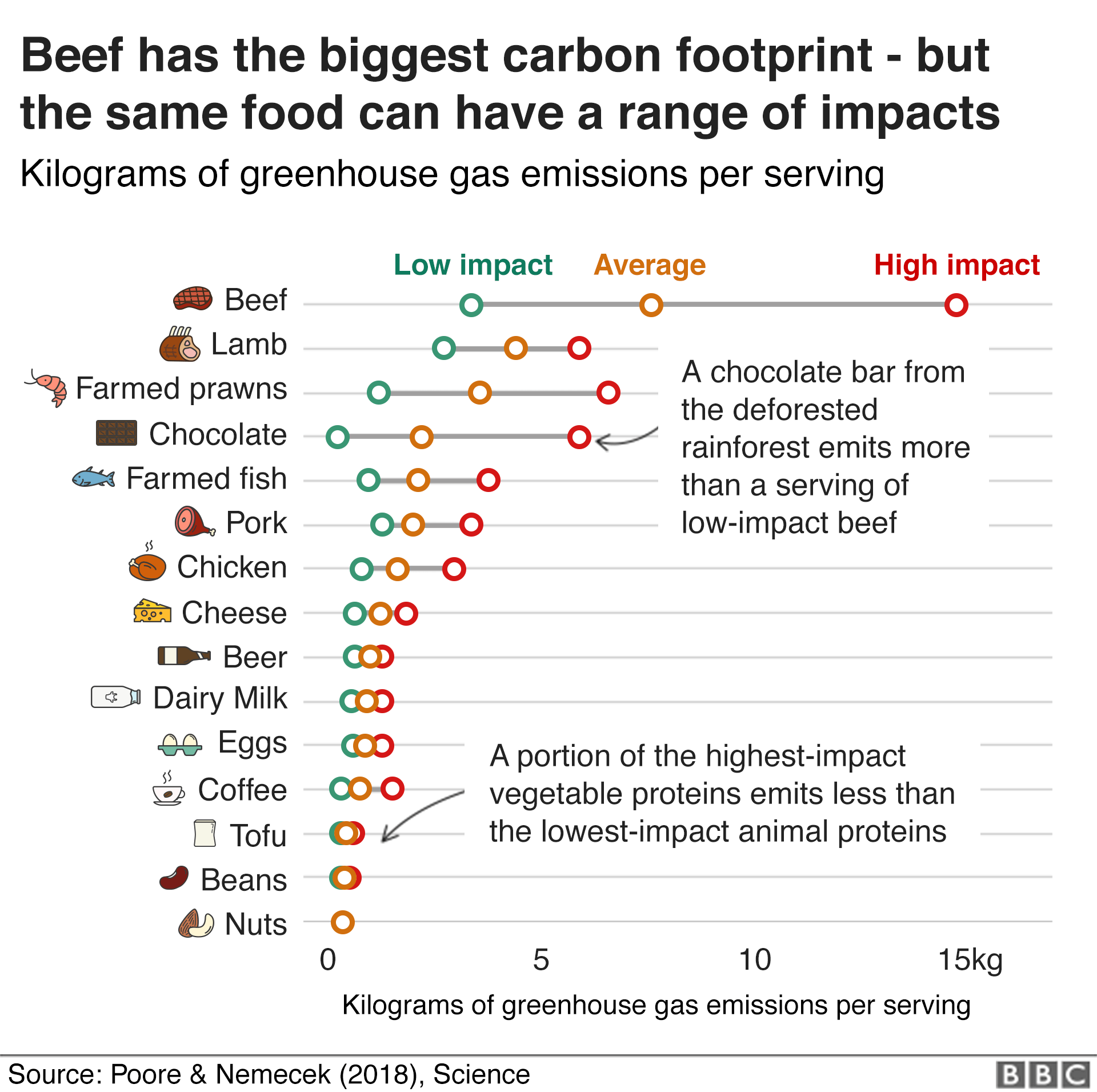



Climate Change Where We Are In Seven Charts And What You Can Do To Help c News




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
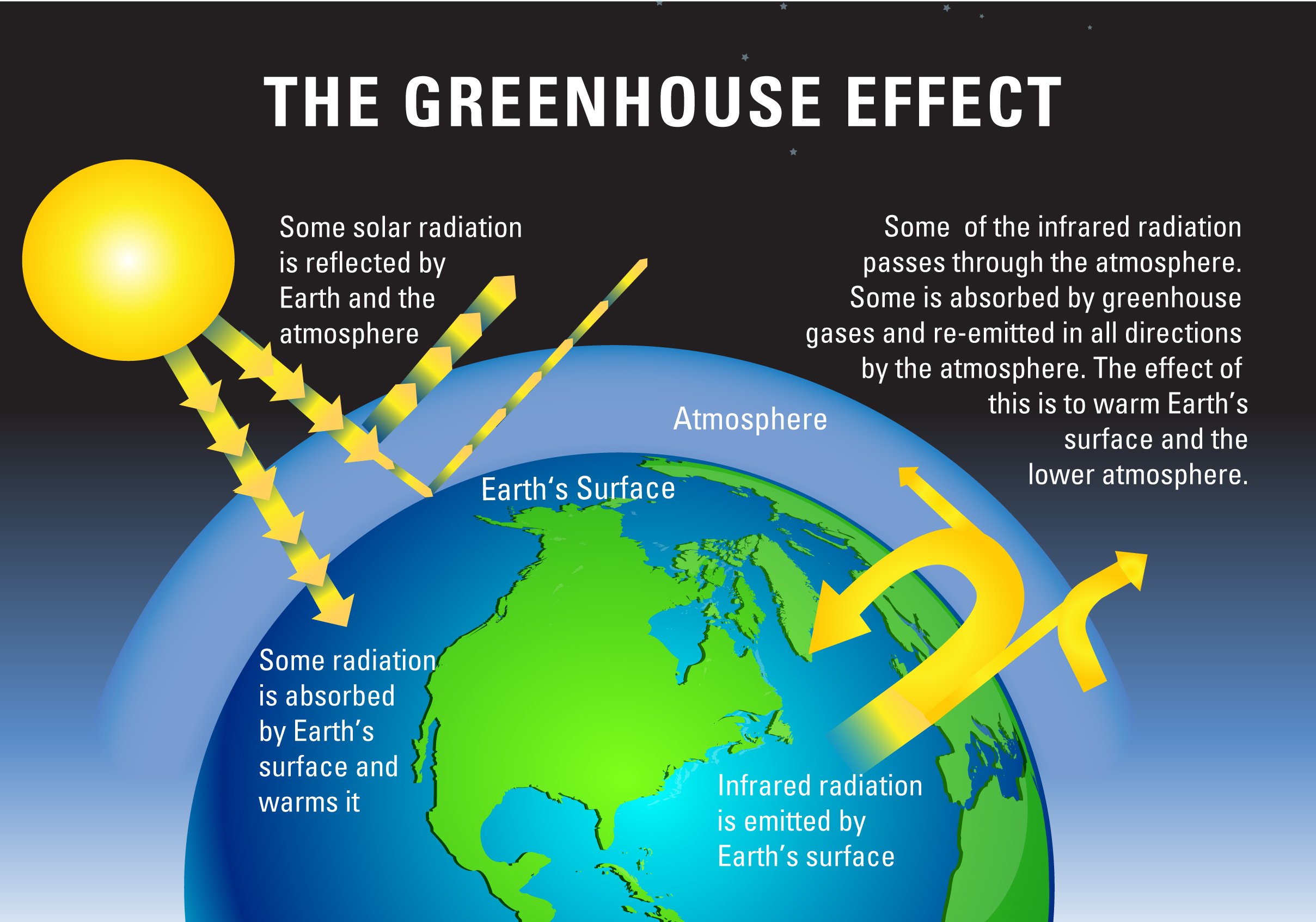



Greenhouse Gases Earth Journalism Network




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students



Methane Emissions In The Oil And Gas Industry American Geosciences Institute




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
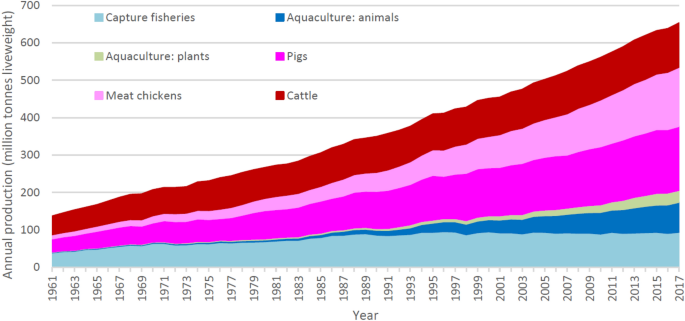



Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Global Aquaculture Scientific Reports




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Emission An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Warming Effect Is Valuable To All Life On Earth Except Maybe Some Microbes Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
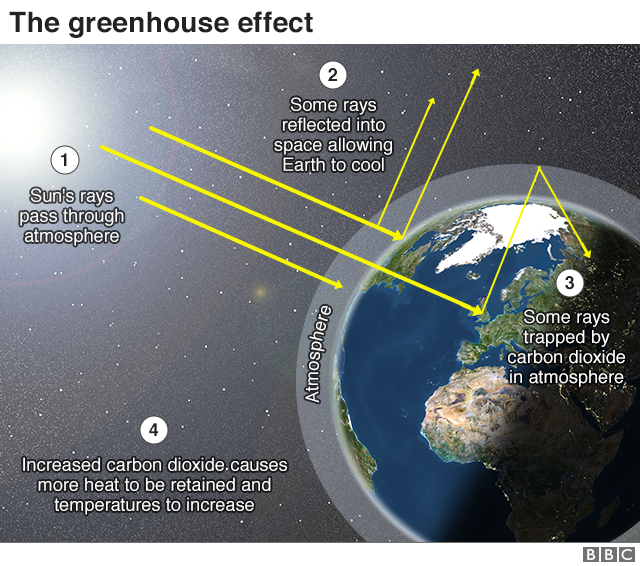



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




What Is Environmental Science Definition And Scope Of The Field Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Science Vincent
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
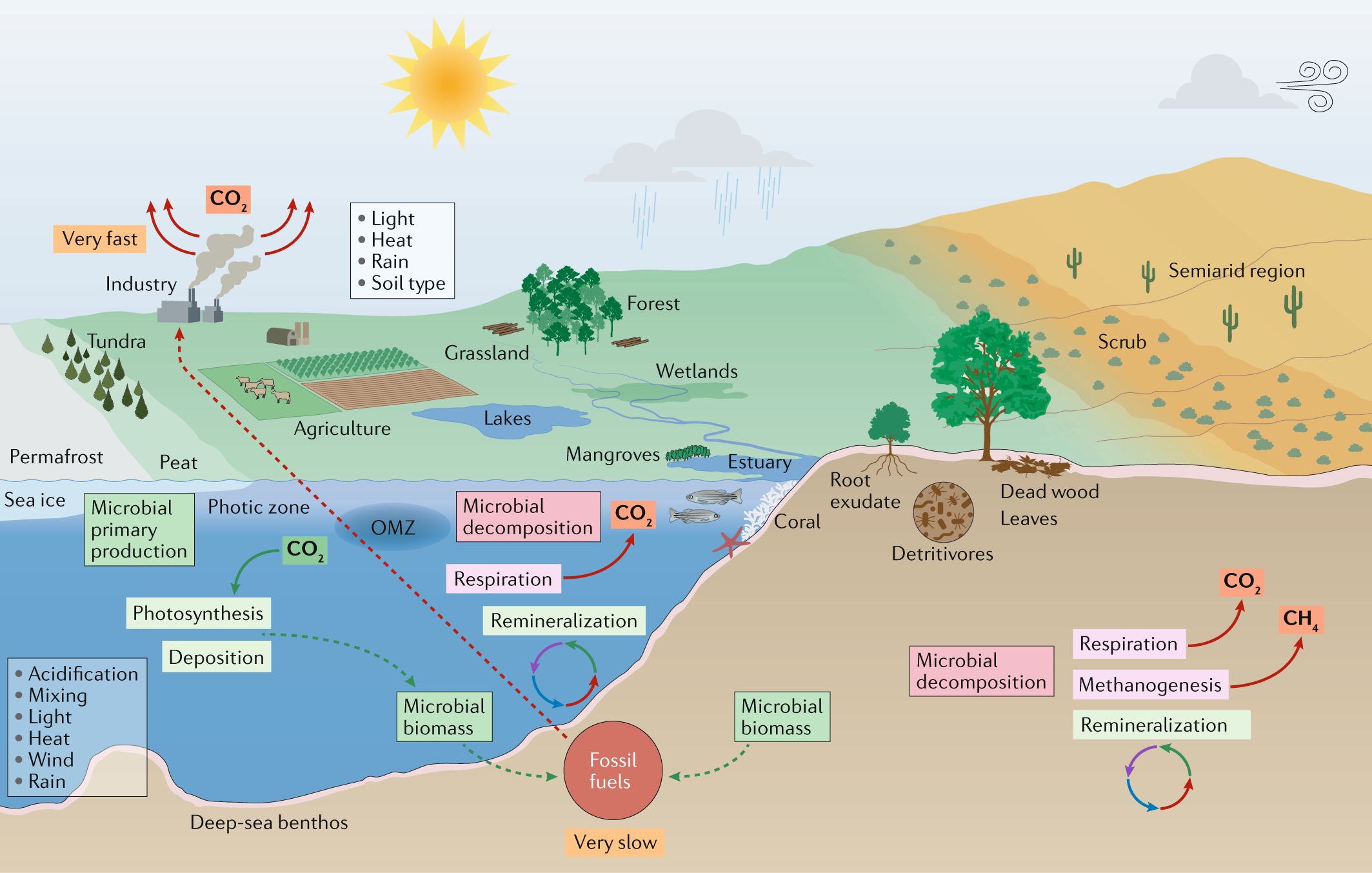



Scientists Warning To Humanity Microorganisms And Climate Change Nature Reviews Microbiology




Green House Effect
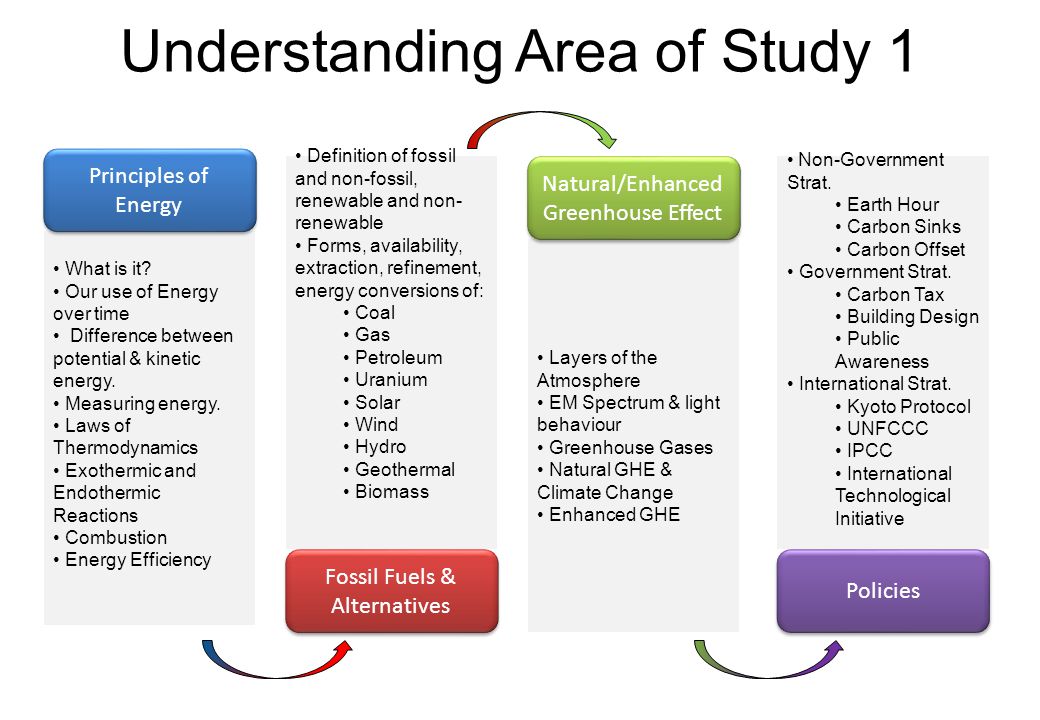



Vce Environmental Science Ppt Download
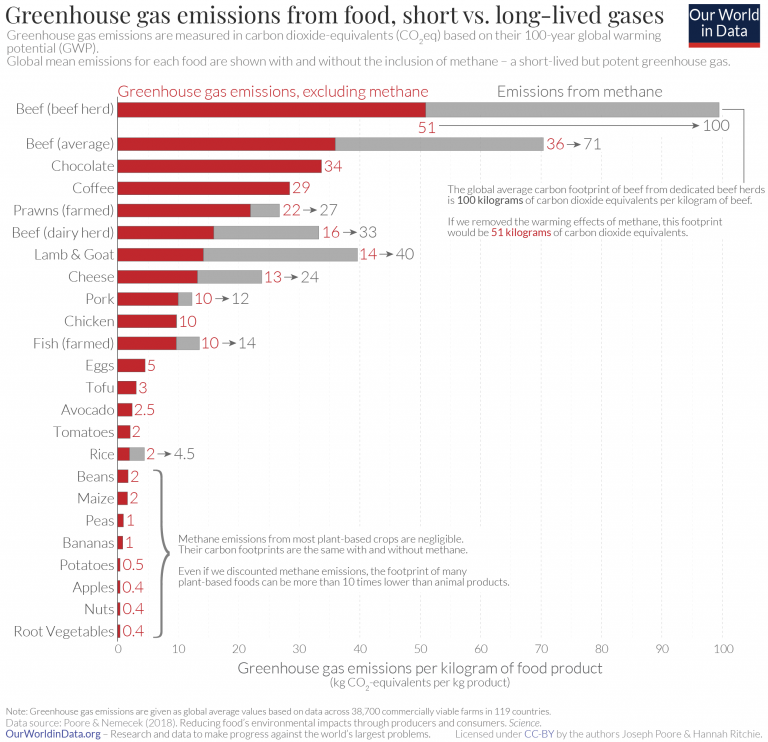



The Carbon Footprint Of Foods Are Differences Explained By The Impacts Of Methane Our World In Data
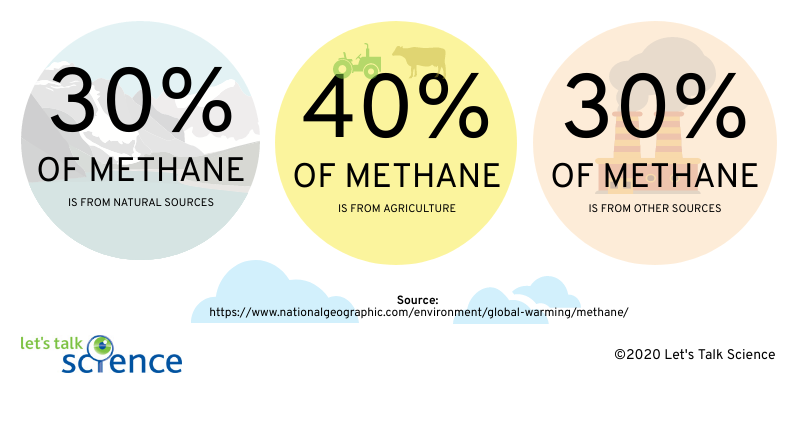



Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



1
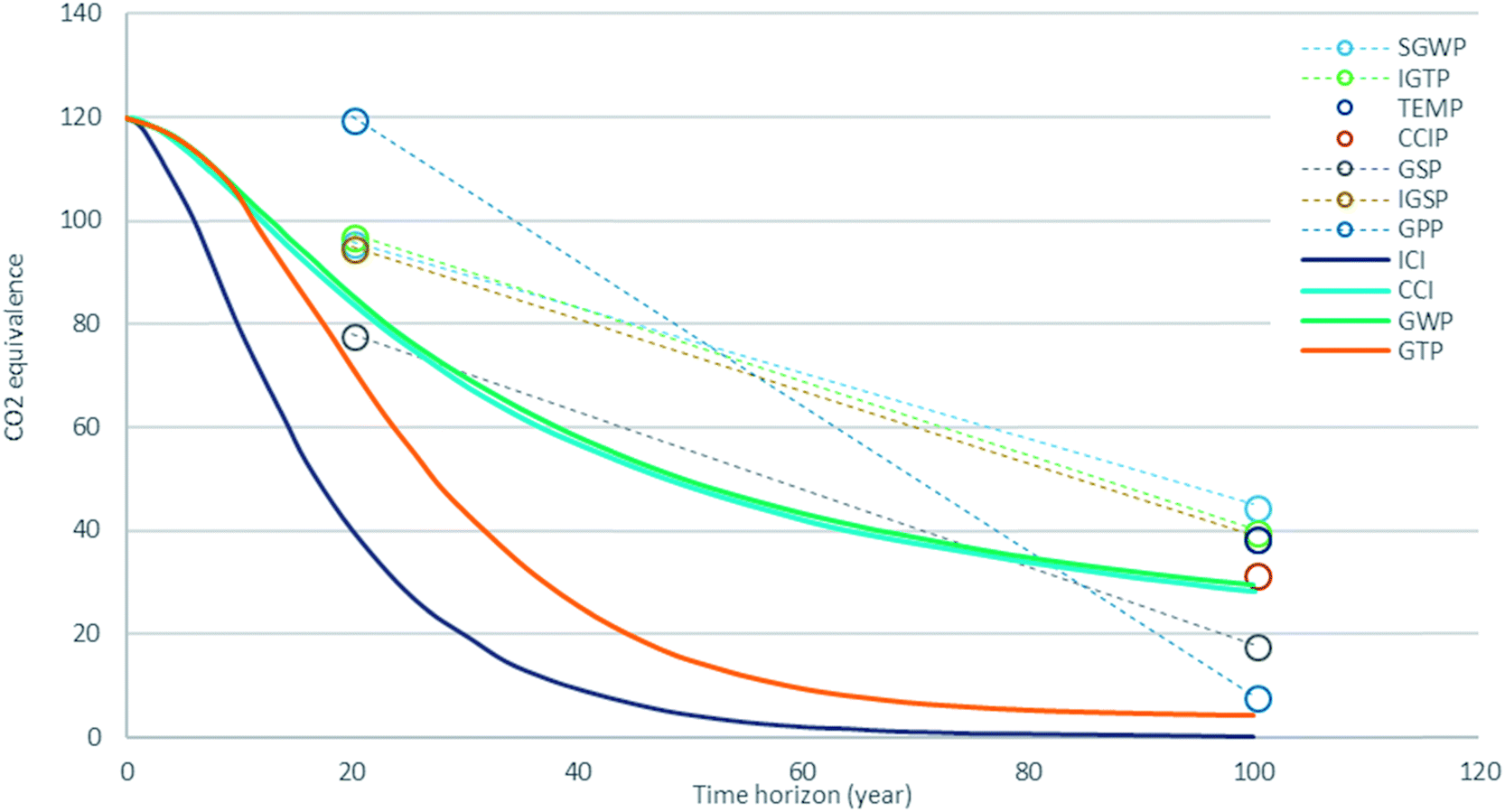



Methane Emissions Choosing The Right Climate Metric And Time Horizon Environmental Science Processes Impacts Rsc Publishing



Css Environmental Sciences Paper 21 Legalversity




Im Doing Environmental Science Questions But Im Not Chegg Com



1



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿